5G technology represents a significant leap forward from its predecessors, 4G and 3G, in wireless communication. The most notable difference lies in its speed: 5G reaches data speeds up to 10 gigabits per second, which can be up to 100 times faster than 4G. This substantial increase enables the handling of more data-intensive applications and services seamlessly. Additionally, 5G dramatically reduces latency to as low as 1 millisecond, compared to 4G’s 20-30 milliseconds, ensuring near-instantaneous communication crucial for real-time military applications.
Beyond speed and latency, 5G surpasses its predecessors in network capacity and flexibility. It supports a significantly higher number of connected devices per square kilometer, making it ideal for dense urban areas and the expanding Internet of Things (IoT). Furthermore, 5G introduces more adaptable network architecture, incorporating technologies like network slicing to create multiple virtual networks within a single physical network. This flexibility enables customized services and efficient resource utilization, distinguishing 5G as a transformative force in wireless technology and its many defense applications.
5G Technology Forecast and Trends
The forecast for 5G technology in the defense market is nothing short of spectacular. The market is estimated to grow from $0.9 billion in 2023 to $2.3 billion in 2028, at a CAGR of 19.9%. The airborne segment has an even more impressive forecast, expected to reach $0.786 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 23.9% during the forecast period. Key players operating in the global 5G defense market include Ericsson, Huawei, Nokia Corporation, Samsung Electronics, NEC Corporation, Thales Group, L3Harris Technologies, Raytheon Technologies Corporation, Ligado Networks, and Wind River Systems.
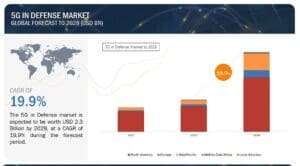
Source: Markets&Markets
Drivers of 5G Adoption in the Military
Several key factors are driving the adoption of 5G technology in military applications:
Rise of autonomous vehicles/drones
The defense industry increasingly relies on autonomous vehicles, drones, and robots, utilizing 5G technology for real-time operations in challenging environments, such as remote enemy surveillance. Countries worldwide, including the U.S., Israel, Russia, China, and India, are heavily investing in unmanned systems for national security, with Europe allocating €7.9 billion for defense R&D in January 2021. These technologies not only enhance operational efficiency but also significantly reduce costs. For example, a U.S. naval destroyer costs $700,000 per day to operate, compared to $15,000 – $20,000 for an autonomous ship. 5G is pivotal for optimizing these autonomous systems, as demonstrated by the U.S. Ignite’s 5G Living Lab pilot program at MCAS Miramar in the area of intelligent video analytics and other global initiatives focusing on 5G-enhanced autonomous defense applications.
Increased governmental support of 5G
Governments worldwide are investing in 5G technology to enhance civilian and property safety, reflecting their commitment to its development. For example, Taiwan’s National Communications Commission (NCC) allocated $948.5 million from 2021 to 2025 to support five telecom operators’ 5G deployment. Such government incentives, including subsidies and R&D grants, assist telecommunications companies and others in the 5G industry in establishing necessary infrastructures and services. The U.S. Department of Defense, for instance, increased its 5G funding to $430 million for both military and civilian applications. Countries like Brazil, China, and India also plan to implement 5G in various sectors. This growing government support is expected to significantly boost the 5G defense market in the coming years.
5G’s technological advancements
The global rise in advanced technologies has spurred the need for fast, reliable networks like 5G to connect devices like robots, sensors, drones, and autonomous vehicles in defense operations. 5G’s real-time connectivity, machine-to-machine communication, and high speed are crucial for surveillance and intelligence activities by security agencies. Its use of the ultra-high frequency (UHF) spectrum (300 MHz to 3 GHz) enables frequency hopping in tactical radios for military and federal use. For example, 5G’s modulation capabilities are vital for border surveillance (requiring high power, low latency) and smart bases (needing low power, long range). Additionally, the development of small cell stations expands network capacity. 5G’s advanced features, including Network Functions Virtualization (NFV), beam-forming antennas, 5G New Radio (NR), Cellular Vehicle-To-Everything (C-V2X) technology, and MIMO antennas, enhance network architecture, coverage, communication, and throughput. These technologies enable immersive services like mobile cloud and ultra-high-definition 3D video, boosting defense mechanism productivity. In this way, 5G’s technological evolution presents significant market growth opportunities in defense.
Benefits of 5G in Military Applications
5G’s next-generation wireless technology brings significant benefits that address the unique and evolving needs of military forces worldwide. They are:
Enhanced Communication and Operational Efficiency: The high data rate and low latency of 5G enable more efficient communication and information exchange in the field, improving command and control capabilities.
Real-time Data Processing and Intelligence: 5G allows for the rapid processing and sharing of large volumes of data, crucial for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) operations.
Autonomous and Remote Operations: The reliable and fast connectivity of 5G supports the deployment of autonomous systems like drones and unmanned vehicles, which are increasingly becoming integral to modern warfare.
Network-Centric Warfare and Interoperability: 5G’s ability to connect numerous devices and systems supports the concept of network-centric warfare, enhancing interoperability among different military branches and allied forces.
Cybersecurity and Resilient Communications: With increasing cyber threats, 5G’s advanced security features are essential in protecting sensitive military communications and ensuring resilient networks.

5G Implementation Challenges in the Defense Sector
While the benefits of 5G in defense are clear, several challenges remain:
Security Concerns: The deployment of 5G networks in defense necessitates stringent security measures to safeguard against espionage, data breaches, and cyber-attacks. In 2020, the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) launched the 5G to NextG Initiative, focusing on developing secure 5G communication networks and exploring ways to protect against vulnerabilities.
Integration with Legacy Systems: The incorporation of 5G technology into existing military infrastructure requires careful planning and investment to ensure compatibility and seamless operation. For example, the British Army’s Bowman tactical communication system faced challenges integrating with new 5G technologies, requiring significant investment and planning.
Spectrum Management: Efficient management of the radio frequency spectrum is critical, considering the crowded nature of these bands and the need for uninterrupted and reliable communication in military operations. The NATO Communications and Information Agency (NCIA) has been working on navigating the complexities of spectrum management to ensure effective communication in military operations.
Geopolitical Implications: The global nature of 5G technology involves considerations around international cooperation, competition, and the potential for technological dependencies on other nations. The United Kingdom in 2020 decided to remove Huawei equipment from its 5G network infrastructure by 2027 due to concerns over national security and the potential risks of dependency on technology from a foreign power.
Future Outlook: 5G and Emerging Technologies in Defense
5G technology represents a watershed moment for the defense industry. With its high-speed, low-latency, and massive connectivity capabilities, 5G is poised to significantly enhance military communication, operational efficiency, and overall strategic capabilities. Companies like Maris are at the forefront of this transformation, developing edge computing solutions that are revolutionizing defense applications by enabling data processing and analysis close to the data source, thereby reducing latency and facilitating real-time responsiveness.
When integrated with 5G networks in defense settings, edge computing allows for swift data processing and decision-making at the network’s edge, crucial for autonomous systems and remote command operations. This combination of 5G and AI edge computing provides a scalable, efficient network architecture for distributed, time-sensitive defense tasks. As we look to the future, the continued advancement and integration of 5G technology in the military domain promise to redefine the landscape of modern warfare.


